- #1
mcfaker
- 43
- 0
Help I am really confused! Orbital overlap in Hcl.
Hi,
The orbital overlap in HCl is due to hybridization between one sp³ oribital from Cl and one s orbital from H.
So why does the following picture say that the orbital overlap is between one p orbital from Cl and one s orbital from H??
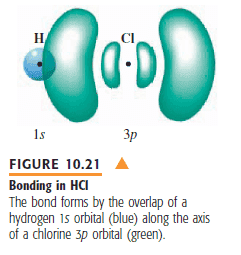
Thanks in advance!
Hi,
The orbital overlap in HCl is due to hybridization between one sp³ oribital from Cl and one s orbital from H.
So why does the following picture say that the orbital overlap is between one p orbital from Cl and one s orbital from H??
Thanks in advance!
Last edited: