Trysse
- 75
- 16
- TL;DR Summary
- I have the following question: Does it make a difference for the surface area of a sphere if the sphere is inward- and outward-oriented?
I usually think of a sphere as the set of all points ##P_x##, that have the identical distance r to some point ##C## which is the center of the sphere. I calculate the surface area ##A## of the sphere as
$$A=4 \pi (C P_x)^2$$
However, what happens if I think of the distance between the points C and Px not just as a distance but as a vector? If I think of the radius of the sphere as a vector, this vector can either point from the surface of the sphere to the center or from the center to the surface
$$ \vec {CP_x} = \vec{r} = \vec{-r} = \vec{P_x C} $$
Does the direction of the radius (i.e. the orientation of the surface) have an influence on the concept of surface area? I was wondering if it makes sense to say:
$$ A=4π \vec{CP_x}^2=−4π \vec{P_xC}^2 $$
I have done a quick search on Google. However, from what I have found, I got the impression, that the surface area is not really an issue that is considered in the context of oriented surfaces. Or did I just search for the wrong keywords?
https://www.google.com/search?q=ori...rome..69i57.6231j0j4&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8
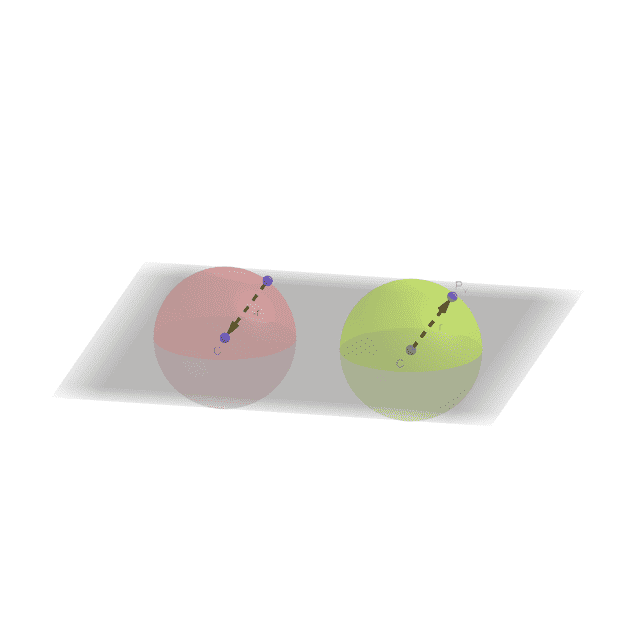
Could I say that the red sphere has a negative surface area while the green sphere has a positive surface area?
$$A=4 \pi (C P_x)^2$$
However, what happens if I think of the distance between the points C and Px not just as a distance but as a vector? If I think of the radius of the sphere as a vector, this vector can either point from the surface of the sphere to the center or from the center to the surface
$$ \vec {CP_x} = \vec{r} = \vec{-r} = \vec{P_x C} $$
Does the direction of the radius (i.e. the orientation of the surface) have an influence on the concept of surface area? I was wondering if it makes sense to say:
$$ A=4π \vec{CP_x}^2=−4π \vec{P_xC}^2 $$
I have done a quick search on Google. However, from what I have found, I got the impression, that the surface area is not really an issue that is considered in the context of oriented surfaces. Or did I just search for the wrong keywords?
https://www.google.com/search?q=ori...rome..69i57.6231j0j4&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8
Could I say that the red sphere has a negative surface area while the green sphere has a positive surface area?
Last edited: