- #1
tarkimos
- 6
- 0
I was wondering if it is possible to convert a projectile motion(velocity, direction, etc) into a (parabolic) equation.
I am programming a motion planner to use in a simple 'game' that I am making.
A formula would be appreciated.
I was thinking something like http://img99.imageshack.us/img99/187/eq220d30dcno9.png
To get the x value I am using the range formula
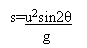
I am then using a similar formula to calculate the total time of flight.
Then I am dividing the range by the total time of flight.
I am programming a motion planner to use in a simple 'game' that I am making.
A formula would be appreciated.
I was thinking something like http://img99.imageshack.us/img99/187/eq220d30dcno9.png
To get the x value I am using the range formula
I am then using a similar formula to calculate the total time of flight.
Then I am dividing the range by the total time of flight.
Attachments
Last edited by a moderator: