- #1
AIDB
- 1
- 0
Homework Statement
Determine the magnitude of the projected component of F1 along the line of action of F2, if the cables each exert a force of 410 N on the post.
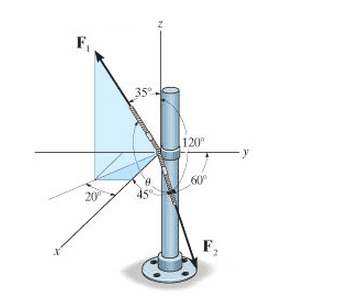 The attempt at a solution
The attempt at a solution
I know how to figure out F2x, F2y, and F2z, but I have no idea how to find F1y and F1x. Also, what does it mean by "F1 along the line of action of F2" and how would I give a final answer in that format?
Thank you
Determine the magnitude of the projected component of F1 along the line of action of F2, if the cables each exert a force of 410 N on the post.
I know how to figure out F2x, F2y, and F2z, but I have no idea how to find F1y and F1x. Also, what does it mean by "F1 along the line of action of F2" and how would I give a final answer in that format?
Thank you