bigpoppapump
- 5
- 0
Im having trouble with the following question regarding Archimedes principle.
A wooden board with an area of 4.55m^2 is dropped into the dead sea (P sea- 1240 kg/m^-3). Calculate the proportion that would float above the surface. (P wood - 812 kg/m^-3).
My understanding is that the volume (V sub) of the submerged object over the total volume (V) of the object is equal to the density (P wood) of the Object over the density (P sea) of the water.
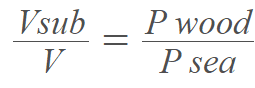
Because the question has given me an area and not a volume or even dimensions to calculate the volume, i am confused as to how to complete the question.
A wooden board with an area of 4.55m^2 is dropped into the dead sea (P sea- 1240 kg/m^-3). Calculate the proportion that would float above the surface. (P wood - 812 kg/m^-3).
My understanding is that the volume (V sub) of the submerged object over the total volume (V) of the object is equal to the density (P wood) of the Object over the density (P sea) of the water.
Because the question has given me an area and not a volume or even dimensions to calculate the volume, i am confused as to how to complete the question.