- #1
Tuccimane
- 1
- 0
1. Physics Lab :
Homework Statement
design, run and report an experiment to calculate A) μs B) μk between a flat bottomed object and a flat surface ( include a section called "theory" in which you formally derive an expression for μs and μk )
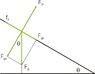
im basically just having troubles deriving , i measured the angle in which my object has started to slide and its about 10 degrees
2. relevant equations
μs :
Fun x = Sum x
0 N = Fg x + Ffs
0 N = mgcos(theta) -μsFN
0 N = mgcos(theta) - μs(mgsin(theta))
mgcos(theta)= μs(mgsin(theta))
mgcos(theta) / mgsin(theta) = μs
μs= cot(theta)
im pretty sure I am supposed to get μs= tan theta, any clue what i did wrong S:
Homework Statement
design, run and report an experiment to calculate A) μs B) μk between a flat bottomed object and a flat surface ( include a section called "theory" in which you formally derive an expression for μs and μk )
im basically just having troubles deriving , i measured the angle in which my object has started to slide and its about 10 degrees
2. relevant equations
The Attempt at a Solution
μs :
Fun x = Sum x
0 N = Fg x + Ffs
0 N = mgcos(theta) -μsFN
0 N = mgcos(theta) - μs(mgsin(theta))
mgcos(theta)= μs(mgsin(theta))
mgcos(theta) / mgsin(theta) = μs
μs= cot(theta)
im pretty sure I am supposed to get μs= tan theta, any clue what i did wrong S:
Last edited by a moderator: