- #1
peter010
- 31
- 0
Homework Statement
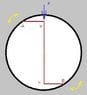
A force F is applied over axis M-N in the such shown position. Both of points A and B are not fixed, and can slides inside the black fixed circle. will the applied force (in the shown position) cause the axis M-N to rotate ? if it is not rotating, then what modification should be made?
Note that the distance A-M = N-B, and M-N's length is double the length of A-M.
Homework Equations
M = F*r
M: Moment
F: Force
R=distance
The Attempt at a Solution
the force will generate equal moments at both points A and B. Anyhow, both of them will cancel each other, and thus no rotation will occur.
What do you think mates?[/B]
Attachments
Last edited: