- #1
gracy
- 2,486
- 83
Why potential at a point can only be obtained by supposing/assuming a positive test charge there?
For example
There was a question
In figure two points A and B are located in a region of electric field.,The potential difference ##VB##-##VA## is
1-positive
2-Negative
3-zero
4-none of the above
the answer is 2-Negative
Apparently the source charge is positive
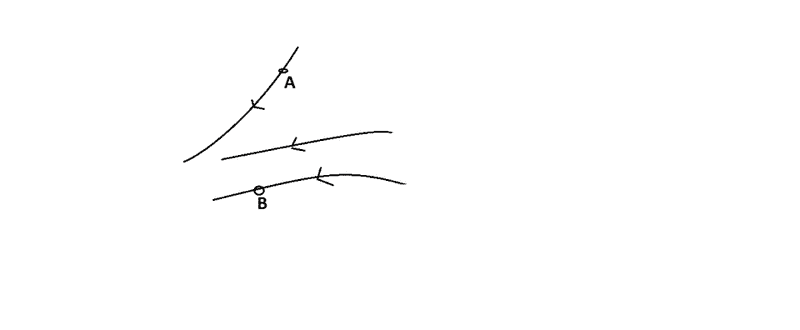
we will only get the answer to be 2-Negative when we would assume positive test charge but if we assume negative test charge at A &B we are going to get answer 1-positive.So is it like we are bound to assume positive charge at points mentioned in question to get whether potential difference is positive or negative?
For example
There was a question
In figure two points A and B are located in a region of electric field.,The potential difference ##VB##-##VA## is
1-positive
2-Negative
3-zero
4-none of the above
the answer is 2-Negative
Apparently the source charge is positive
we will only get the answer to be 2-Negative when we would assume positive test charge but if we assume negative test charge at A &B we are going to get answer 1-positive.So is it like we are bound to assume positive charge at points mentioned in question to get whether potential difference is positive or negative?