- #1
FlorenceC
- 24
- 0
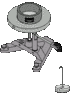
There is an experimental set up that looks like the attitude file.
1) for mass hanging down the pulley write Newton's second law
2)since the sensor measures α find substitute a with a variable containing α
3) for the drum (horizontal pulley) find another equation for torque other than τ = Iα
4) combine eqn 1-3 to find an equation for τ via, T, a, r and α
The attempt at a solution
1) ma=mg-T
2) a = αr
3) τ = Tr
4) τ = m(g-αr) r
1) for mass hanging down the pulley write Newton's second law
2)since the sensor measures α find substitute a with a variable containing α
3) for the drum (horizontal pulley) find another equation for torque other than τ = Iα
4) combine eqn 1-3 to find an equation for τ via, T, a, r and α
The attempt at a solution
1) ma=mg-T
2) a = αr
3) τ = Tr
4) τ = m(g-αr) r