- #1
tj00343
- 63
- 0
Hello Everyone,
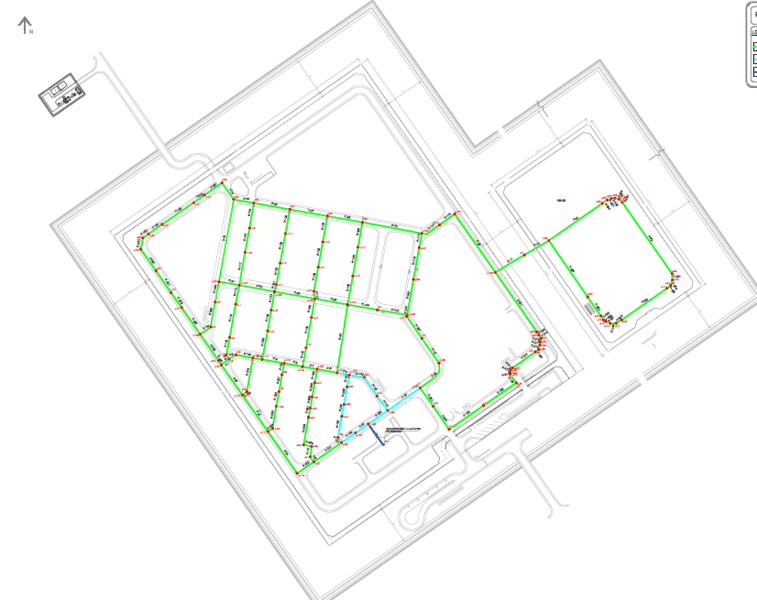
I've been tasked with verifying the pump external static pressure for an infrastructure water supply network. The network is a series of loops as shown in the image attached . According to the calculation notes done by the designer, the design of the network was done in watercad by taking the total flow requirement in the network and dividing it evenly to all nodes in the network in watercad.
My attempt at solving this problem:
I was thinking I would put the flow required at each building in water cad at the node closest to it and put the actual pipe sizes instead of the calculated ones and rerun the model in order to find which line has the highest pressure drop and the pump would be sized according to the pressure drop in this line. However, my problem is I don't know on what basis to calculate the flow for each building as I am not familiar with infrastructure networks and I assume using fixture units would result in a number that is quite over sized .Also, the design is based on a french norm DTU (NF DTU 60.11 P1-1) which I am not familiar with.
Any help or guidance would be appreciated
I've been tasked with verifying the pump external static pressure for an infrastructure water supply network. The network is a series of loops as shown in the image attached . According to the calculation notes done by the designer, the design of the network was done in watercad by taking the total flow requirement in the network and dividing it evenly to all nodes in the network in watercad.
My attempt at solving this problem:
I was thinking I would put the flow required at each building in water cad at the node closest to it and put the actual pipe sizes instead of the calculated ones and rerun the model in order to find which line has the highest pressure drop and the pump would be sized according to the pressure drop in this line. However, my problem is I don't know on what basis to calculate the flow for each building as I am not familiar with infrastructure networks and I assume using fixture units would result in a number that is quite over sized .Also, the design is based on a french norm DTU (NF DTU 60.11 P1-1) which I am not familiar with.
Any help or guidance would be appreciated