user_18041984
- 3
- 0
Hello dear forum members.
I've run into some problem and I'm hoping someone here can give me a hint on how to solve it.
There is an electrochemical method for separating some binary metal alloys based on the cementation phenomenon. I'll show you how it works with the example of separatting brass.
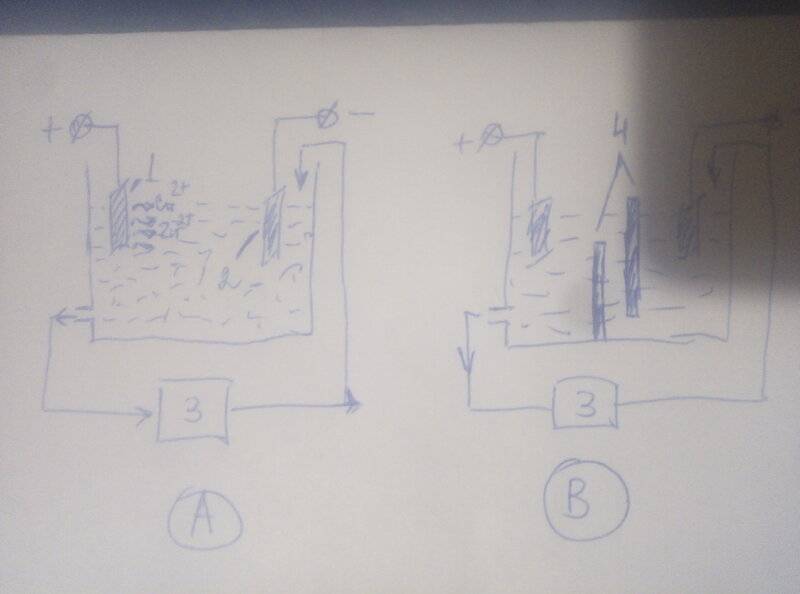
So, in figure A we have an anode made of zinc-copper alloy (1). The cathode (2) is made of zinc. The electrodes are in a solution of zinc sulfate, voltage is applied to them. The solution formed at the anode, containing copper ions and zinc ions, is pumped out by a pump into the cementator (3), which is a container filled with metallic zinc in the form of shavings or pieces. Since copper has a more electropositive potential, contact deposition of copper occurs in the cementator according to the reaction Cu2+ + Zn = Cu + Zn2+. The solution, freed from copper ions and containing only zinc ions, is fed into the cathode region, where only zinc is deposited on the cathode.
But, if the bath is assembled in this form, then the possibility is not ruled out that copper ions will enter the cathode region directly, bypassing the cementator. Then the cathodic zinc will be contaminated with copper.
Before me is the task of assembling such a bath in practice. In order to exclude direct contact of the anode solution with the cathode, I thought to introduce partitions (4) into the bath, as in Figure B. But then I realized that with these partitions, the electrical resistance of the bath and the power consumption will greatly increase. As a result, in order to provide the required current strength, I will have to apply a huge voltage and it will heat up, which is not good.
To be honest, I'm at a dead end. There are no partitions - there is mixing; there are partitions - there is resistance. Can anyone advise on the correct practical design of this bathtub?
I've run into some problem and I'm hoping someone here can give me a hint on how to solve it.
There is an electrochemical method for separating some binary metal alloys based on the cementation phenomenon. I'll show you how it works with the example of separatting brass.
So, in figure A we have an anode made of zinc-copper alloy (1). The cathode (2) is made of zinc. The electrodes are in a solution of zinc sulfate, voltage is applied to them. The solution formed at the anode, containing copper ions and zinc ions, is pumped out by a pump into the cementator (3), which is a container filled with metallic zinc in the form of shavings or pieces. Since copper has a more electropositive potential, contact deposition of copper occurs in the cementator according to the reaction Cu2+ + Zn = Cu + Zn2+. The solution, freed from copper ions and containing only zinc ions, is fed into the cathode region, where only zinc is deposited on the cathode.
But, if the bath is assembled in this form, then the possibility is not ruled out that copper ions will enter the cathode region directly, bypassing the cementator. Then the cathodic zinc will be contaminated with copper.
Before me is the task of assembling such a bath in practice. In order to exclude direct contact of the anode solution with the cathode, I thought to introduce partitions (4) into the bath, as in Figure B. But then I realized that with these partitions, the electrical resistance of the bath and the power consumption will greatly increase. As a result, in order to provide the required current strength, I will have to apply a huge voltage and it will heat up, which is not good.
To be honest, I'm at a dead end. There are no partitions - there is mixing; there are partitions - there is resistance. Can anyone advise on the correct practical design of this bathtub?