- #1
christopher.s
- 32
- 4
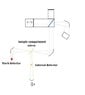
I am trying to interface a detector system to a FT-IR spectrometer. The spectrometer uses off-axis parabolic mirrors to focus light in the center of a sample compartment, where it diverges and again strikes an off axis parabolic mirror, focusing it on a detector. I would like to place a plane mirror at a 45° angle, at the focal point of the first mirror. My question is, what kind of beam divergence can I expect with this setup? The detector element itself will be housed in a dewar behind some windows and filters, approximately 6-8" from the mirror in the sample compartment. There is a compound parabolic concentrator, located about 3inches in front of the detector, with a .500" entrance aperture. Can I expect reasonable signal from this setup? This will be used in the IR, from about 20-700cm-1. Will atmospheric interference be significant? I have attached a quick sketch of the outline of the system.
Thanks!
https://www.physicsforums.com/attachment.php?attachmentid=57447&stc=1&d=1365048951
Thanks!
https://www.physicsforums.com/attachment.php?attachmentid=57447&stc=1&d=1365048951