- #1
hadeel35queen
- 1
- 0
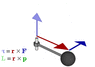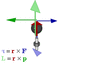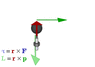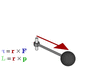
Hi , i really have an important question , first Iam an Arabic girl so my English may cannot be perfect ! SO ,, we took the TORQUE lesson in school and i found it hard to understand , can anyone JUST gives me some steps to understand it .
AND THANK YOU FOR EVERY ONE ..
AND THANK YOU FOR EVERY ONE ..