spaghetti3451
- 1,311
- 31
Consider the scattering process ##W^{+}W^{-} \to W^{+}W^{-}##. This process is mediated in the Standard Model by
1. a four-##W## scattering,
2. ##Z##-boson exchange,
3. Higgs exchange.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Let us consider the diagrams for ##Z##-boson exchange:
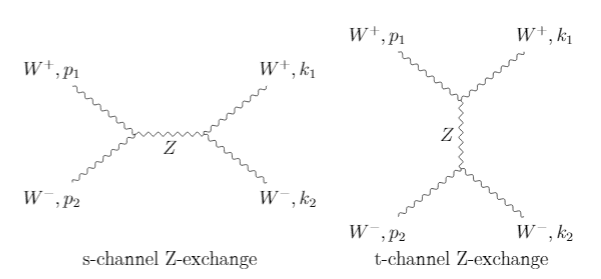 Why is there a relative minus sign between the matrix elements for the two diagrams?
Why is there a relative minus sign between the matrix elements for the two diagrams?
1. a four-##W## scattering,
2. ##Z##-boson exchange,
3. Higgs exchange.
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Let us consider the diagrams for ##Z##-boson exchange: