- #1
bugatti79
- 794
- 1
Hi Folks,
I am struggling to see how eqn 4.1.17 is arrived at using using eqn 4.1.10 at bottom of attachment. Its not clear to me what [tex]\frac{d \phi}{dt}[/tex] is...apart from what is given in eqn 2.1.30...
Any ideas?
Thanks
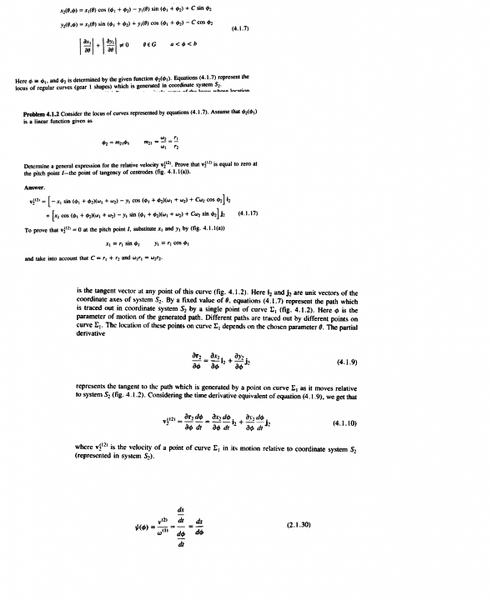
I am struggling to see how eqn 4.1.17 is arrived at using using eqn 4.1.10 at bottom of attachment. Its not clear to me what [tex]\frac{d \phi}{dt}[/tex] is...apart from what is given in eqn 2.1.30...
Any ideas?
Thanks