- #1
Ketler
- 3
- 0
Hello,
I've got one problem with fluid flow reaction force which acts on compressor. I hope you can help me with that.
Here is a sketch to my question:
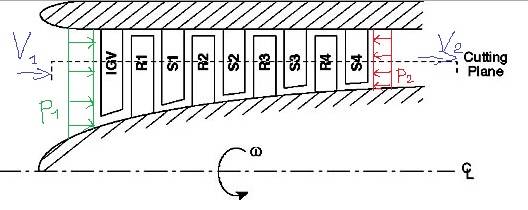
I wonder in which direction resultant force will be directed.
I understand that air is flowing from left to right with inlet velocity V1.
Therefore force which gas exerts on compressor inlet is equal to:
F1s=P1*A1,
where:
P1 - static force on compressor inlet;
A1 - compressor inlet area.
F1s it is a force which compressor inlet feels when V1=0.
When V1 differ from 0, there is also dynamic force:
F1d = 1/2*rho*V1^2
Therefore total force which acts on inlet is equal to:
F1=F1s + F1d.
This is clear. I have problem with compressor outlet.
First, why exit pressures P2, is directed towards the compressor inlet (from right to left)?
It shouldn't be like in inlet section (from left to right)? Could you explain me why is that?
In textbooks there is equation for reaction force at compressour outlet:
F2=F2s + F2d,
where:
F1d = 1/2*rho*V2^2
And here is my second question:
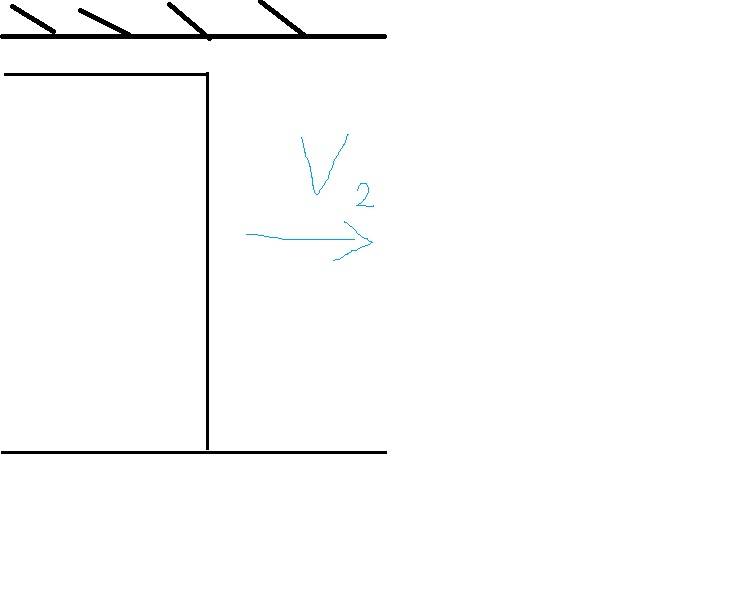
How gas with velocity V2 can act on compressor when it is after the last rotor/stator in the compressor?
I understand when gas with velocity V2 hits the last rotor/stator leading edge, it exerts than force which pull the compressor from left to right, but how gas which is after the last blade can affect the compressor?
I know that there are very silly questions, but I hope you can help me with that.
Regards,
Lukasz.
I've got one problem with fluid flow reaction force which acts on compressor. I hope you can help me with that.
Here is a sketch to my question:
I wonder in which direction resultant force will be directed.
I understand that air is flowing from left to right with inlet velocity V1.
Therefore force which gas exerts on compressor inlet is equal to:
F1s=P1*A1,
where:
P1 - static force on compressor inlet;
A1 - compressor inlet area.
F1s it is a force which compressor inlet feels when V1=0.
When V1 differ from 0, there is also dynamic force:
F1d = 1/2*rho*V1^2
Therefore total force which acts on inlet is equal to:
F1=F1s + F1d.
This is clear. I have problem with compressor outlet.
First, why exit pressures P2, is directed towards the compressor inlet (from right to left)?
It shouldn't be like in inlet section (from left to right)? Could you explain me why is that?
In textbooks there is equation for reaction force at compressour outlet:
F2=F2s + F2d,
where:
F1d = 1/2*rho*V2^2
And here is my second question:
How gas with velocity V2 can act on compressor when it is after the last rotor/stator in the compressor?
I understand when gas with velocity V2 hits the last rotor/stator leading edge, it exerts than force which pull the compressor from left to right, but how gas which is after the last blade can affect the compressor?
I know that there are very silly questions, but I hope you can help me with that.
Regards,
Lukasz.