Voltux
- 29
- 3
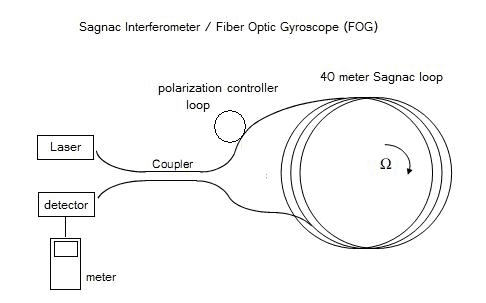
How does one determine which direction a sagnac interferometer is turning in a fiber optic gyro? ("FOG")
I have been reading about them and found some DIY examples where the output is taken using a photo-diode. Now my understanding is that these photo-diodes are simply measuring intensity but isn't the output of the interferometer simply a fringe pattern?
Any additional information, sources, references, imagery, or calculations would be incredibly appreciated.
Thank you!
Reference 1 - Sagnac Interferometer: http://www.conspiracyoflight.com/Sagnac/Sagnac.html
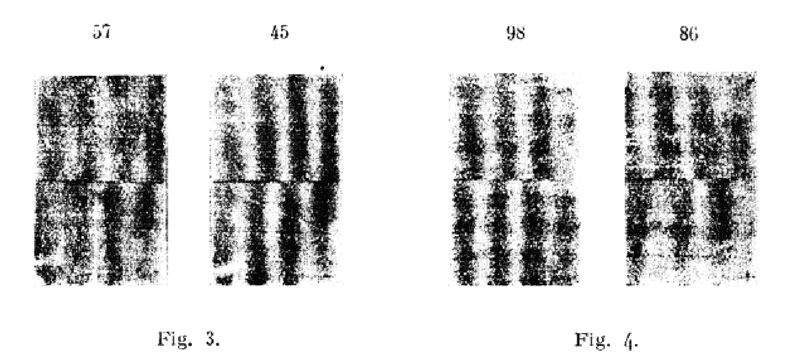
 Reference 2 - Fringe Pattern Generated (CW + CCW): http://www.conspiracyoflight.com/pd...ed_on_a_Platform_in_Uniform_Motion_(1942).pdf
Reference 2 - Fringe Pattern Generated (CW + CCW): http://www.conspiracyoflight.com/pd...ed_on_a_Platform_in_Uniform_Motion_(1942).pdf
I have been reading about them and found some DIY examples where the output is taken using a photo-diode. Now my understanding is that these photo-diodes are simply measuring intensity but isn't the output of the interferometer simply a fringe pattern?
Any additional information, sources, references, imagery, or calculations would be incredibly appreciated.
Thank you!
Reference 1 - Sagnac Interferometer: http://www.conspiracyoflight.com/Sagnac/Sagnac.html