- #1
Worldline
- 23
- 0
Hi
we know the relation between wavelength, frequency and energy :
The greater the energy, the larger the frequency and the shorter (smaller) the wavelength -> E=h[itex]\upsilon[/itex]
On the other side, SAR is common property that measures absorbed energy.
Now if we calculating SAR for human brain tissue , we would have such graph :
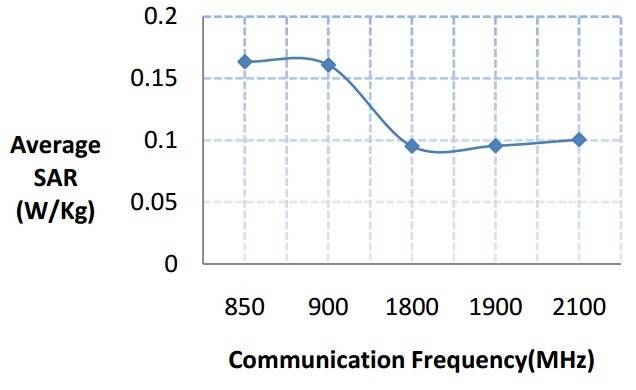
But i don't understand why it behaves like that , why SAR doesn't increase with frequency ?
we know the relation between wavelength, frequency and energy :
The greater the energy, the larger the frequency and the shorter (smaller) the wavelength -> E=h[itex]\upsilon[/itex]
On the other side, SAR is common property that measures absorbed energy.
Now if we calculating SAR for human brain tissue , we would have such graph :
But i don't understand why it behaves like that , why SAR doesn't increase with frequency ?