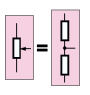- #1
eddysd
- 39
- 0
Really simple problem but:
If you have a circuit with a power supply, a potentiometer and an output voltage taken from midway down the potentiometer and just after it; would this act like a potential divider with the potentiometer acting as two resistors?
If you have a circuit with a power supply, a potentiometer and an output voltage taken from midway down the potentiometer and just after it; would this act like a potential divider with the potentiometer acting as two resistors?