- #1
kylie22
- 3
- 0
hi all,
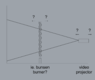
i would like to set up a small lab experiment to try to create visible "terrestrial scintillation", whereby one can see fluctuations in air density (turbulent air), like the rear of the jet in this image:

i have sketched a small setup before i begin; the test will send a projected image through the heat to map what it does to the image as it hits the wall.
i am wondering how best to accentuate the visibility, is it about:
- having lots of heat from a source;
- mixing hot air with cold air;
- controlling the distances between wall, heat source and projector?

kylie
i would like to set up a small lab experiment to try to create visible "terrestrial scintillation", whereby one can see fluctuations in air density (turbulent air), like the rear of the jet in this image:
i have sketched a small setup before i begin; the test will send a projected image through the heat to map what it does to the image as it hits the wall.
i am wondering how best to accentuate the visibility, is it about:
- having lots of heat from a source;
- mixing hot air with cold air;
- controlling the distances between wall, heat source and projector?
kylie