- #1
mulothecook
- 6
- 0
Hello there.
I am stuck trying to figure out the voltage gain of a cascode amplifier from a small signal analysis. The circuit seems to be under-determined for reasons I do not understand or maybe I am missing the perfectly obvious.
Here's my small signal model:
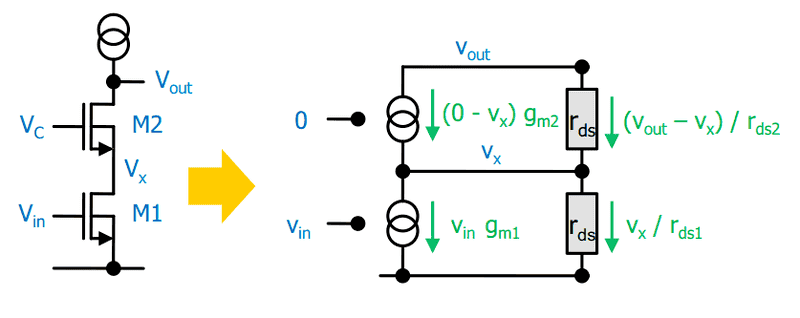
The only relation I can deduce without using further unknown quantities is the KCL for the vx node:
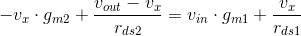
However, I need another relation to eliminate vx in order to solve for vout/vin. The small signal analysis without the cascode works just fine. May I kindly ask somebody to clarify this?M
I am stuck trying to figure out the voltage gain of a cascode amplifier from a small signal analysis. The circuit seems to be under-determined for reasons I do not understand or maybe I am missing the perfectly obvious.
Here's my small signal model:
The only relation I can deduce without using further unknown quantities is the KCL for the vx node:
However, I need another relation to eliminate vx in order to solve for vout/vin. The small signal analysis without the cascode works just fine. May I kindly ask somebody to clarify this?M