- #1
another813
- 1
- 0
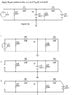
Apply Superposition to the circuit of Fig (5) to find i3.
i3 is above the 100v source flowing upward.
I have provided the problem on the attachment.
Like the theorem states, I have the 3 different re-drawings with the sources short circuited and removed. I have been surfing for hours trying to find a similar problem to help me out.
I do understand how to do like it is on this website http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objID=DCE3802 .
I am just confused on what I should do next on my problem. I am not expecting someone to just give me the answer rather to just give me a hint on what I need to next.
Thanks in Advanced.
-Daniel
i3 is above the 100v source flowing upward.
I have provided the problem on the attachment.
Like the theorem states, I have the 3 different re-drawings with the sources short circuited and removed. I have been surfing for hours trying to find a similar problem to help me out.
I do understand how to do like it is on this website http://www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objID=DCE3802 .
I am just confused on what I should do next on my problem. I am not expecting someone to just give me the answer rather to just give me a hint on what I need to next.
Thanks in Advanced.
-Daniel