- #1
physicsed
- 52
- 0
Homework Statement
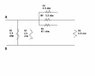
https://www.physicsforums.com/attachment.php?attachmentid=11955&stc=1&d=1197437955
Find the equivalent resistance between points A and B shown in the link above
Homework Equations
for parallel, equivalent resistance is =1/R1 +1/R2 +1/R3...
equivavalent resistance for series is = R1 + R2 + R3
The Attempt at a Solution
i believe they are all parallel or R3, R4, R5, and R6 are series becouse they depend on each other