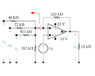
- #1
ElijahRockers
Gold Member
- 270
- 10
Homework Statement
Va = 4V
Vb = 9V
Vc = 13V
Vd = 8V
The 220k resistor is replaced by a variable resistor Rf.
What value of Rf will cause the Op Amp to saturate? Note: 0 ≤ Rf ≤ ∞
When Rf obtains that value, what will be the current flowing into the output terminal of the op amp?
The Attempt at a Solution
In my notes, it says Vcc/A = Vp - Vn is the condition that will cause saturation but I'm not sure where to go with that from here.
I solved the circuit for currents and everything, but I'm not sure how to calculate what Rf should be to make Vcc/A = Vp - Vn.
Vcc/A is just 15/(10^6) as i understand it but Vp = Vn because of the virtual short...
And in this diagram, Vn = 8 right?
Sooo, I solved for Vp and got 8.000015V, then I divided that by the current that is flowing through the 220k resistor to see what the new resistance should be, and it comes out to 219981, which is basically just 220k anyway.
What am I doing wrong?
EDIT: I should show some of my calculations. Using KCL, I found that the output voltage using the 220k resistor is 14V.
Last edited: