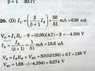- #1
munna007
- 34
- 0
solvethis question please
hello to all...
i m having some doubts in solution of this question...
what i know about this ckt is that this is pnp transistor. +9 volt is connected to emitter (where arrow made) and -9 volt is connected to collector.
i think voltage emitter Voltage Ve should be equal to +9 volt , because current source is not dropping any voltage . but in solution part its found something else i.e 1.68 ...
why is it ? please clear my doubt
hello to all...
i m having some doubts in solution of this question...
what i know about this ckt is that this is pnp transistor. +9 volt is connected to emitter (where arrow made) and -9 volt is connected to collector.
i think voltage emitter Voltage Ve should be equal to +9 volt , because current source is not dropping any voltage . but in solution part its found something else i.e 1.68 ...
why is it ? please clear my doubt