- #1
nassir
- 1
- 0
Hi every one,
I am a fluent user, & I need help to illustrate something concerning the mass flow inlet.
when I want to inject a gas ''for example" I want then to change the parameters from normal on the shape into leaded by a 'direction vector', so I choose direction vector instead of Normal.then I have to fill in the new fields that appears ''Axial components" & " radial component".
Here is my question! can anyone tell me what those two fields refers for
for example, my steering angle will be ' 20° ' so can I write in the axial & radial components? are they refers to Sin & cos?
Please let me know !
Thanks in advance
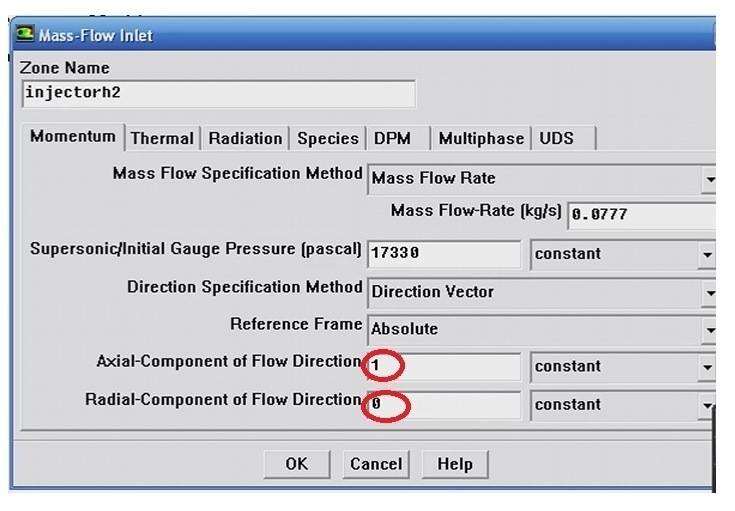
I am a fluent user, & I need help to illustrate something concerning the mass flow inlet.
when I want to inject a gas ''for example" I want then to change the parameters from normal on the shape into leaded by a 'direction vector', so I choose direction vector instead of Normal.then I have to fill in the new fields that appears ''Axial components" & " radial component".
Here is my question! can anyone tell me what those two fields refers for
for example, my steering angle will be ' 20° ' so can I write in the axial & radial components? are they refers to Sin & cos?
Please let me know !
Thanks in advance