- #1
Mugged
- 104
- 0
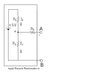
Hey I can't figure out how to convert the below circuit into its thevenin equivalent. I am used to having two points to work with, but in this circuit there is only one and a ground.
http://img715.yfrog.com/i/13332492.jpg/
for some reason the image doesn't show up on my screen; if that's the case for you, the link is below
http://img715.yfrog.com/i/13332492.jpg/
help appreciated!
http://img715.yfrog.com/i/13332492.jpg/
for some reason the image doesn't show up on my screen; if that's the case for you, the link is below
http://img715.yfrog.com/i/13332492.jpg/
help appreciated!
Last edited by a moderator: