- #1
sciontc03
- 10
- 0
Homework Statement
I need help with this problem please. My partner and I have stared at this problem and keep going in circles and can't seem to figure out how to work this problem. Please help!
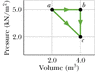
One mole of an ideal diatomic gas undergoes a transition from a to c along the diagonal path in the figure attached.
During the transition, what is the change in internal energy of the gas?
How much energy is added to the gas as heat?
How much heat is required if the gas goes from a to c along the indirect path abc?
Homework Equations
pv=nrt
E=Q-W
The Attempt at a Solution
I don't even know where to begin. Please help.