- #1
baby_1
- 159
- 15
Hello
I have some questions to understand much more better the Gauss's law in Cartesian coordinate.
1-when can we use Gauss's law and it's integral to solve a question easier in Cartesian coordinate?
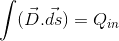
2-Is it difference to use a cylindrical or cube shape for a plane that disturbed some charges(P0) on it?
3-If we want to use Gauss's law for a plane we should use symmetric Gaussian shape or not?(see these two pictures)
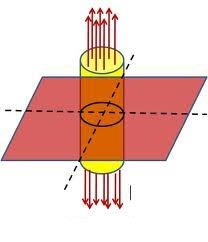
or
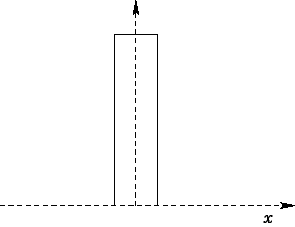
4-Should we define electric filed direction ? if yes , how should define electric filed direction?
(some examples a,b) it's direction is it related where we want to define electric filed value?
(a)
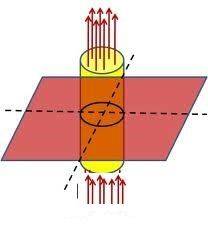
(b)
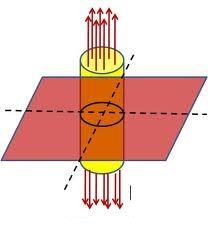
I have some questions to understand much more better the Gauss's law in Cartesian coordinate.
1-when can we use Gauss's law and it's integral to solve a question easier in Cartesian coordinate?
2-Is it difference to use a cylindrical or cube shape for a plane that disturbed some charges(P0) on it?
3-If we want to use Gauss's law for a plane we should use symmetric Gaussian shape or not?(see these two pictures)
or
4-Should we define electric filed direction ? if yes , how should define electric filed direction?
(some examples a,b) it's direction is it related where we want to define electric filed value?
(a)
(b)