- #1
fonseh
- 529
- 2
Homework Statement
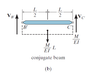
For the circled beam , we can see that for both cases , the load are loaded in the same way ... Why the M / EI diagram for the first case is different from the second case ? Why for the first case , it's symmetric loading ? For the second case , it's antisymmetric loading ?
Homework Equations
The Attempt at a Solution
I think the second case is wrong . Only the first case make sense . From the figure , we can see that the load P is applied at the midspan of AB and CD . So . it's symmetric loading , am i right ?