- #1
AHMEDbr
- 16
- 0
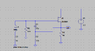
Homework Statement
I am designing a local oscillator ( clapp ) whose frequency needs to be kept constant even with varying temperatures , this oscillator have an output frequency 150 MHZ , and power supply 3.3 V
Homework Equations
which temperature compensation circuit must be used with this oscillator ?