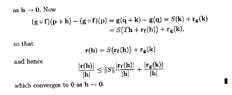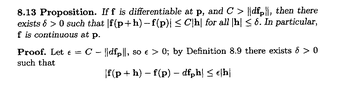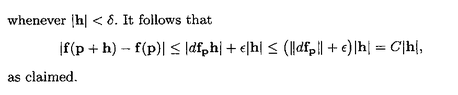- #1
Math Amateur
Gold Member
MHB
- 3,998
- 48
I am reading Andrew Browder's book: "Mathematical Analysis: An Introduction" ... ...
I am currently reading Chapter 8: Differentiable Maps and am specifically focused on Section 8.2 Differentials ... ...
I need some help in order to fully understand the proof of Theorem 8.15 ...
Theorem 8.15 and its proof read as follows:
View attachment 9412
View attachment 9413
In the above proof by Browder we read the following:" ... ... Then \(\displaystyle |k| \leq C |h|\) for \(\displaystyle |h|\) sufficiently small, if \(\displaystyle C \gt \| T \|\), by Proposition 8.13; it follows that
\(\displaystyle \frac{ r_g ( k(h) ) }{ |h| } \to 0\) as \(\displaystyle h \to 0\). ... ... "
My question is as follows:Can someone demonstrate formally and rigorously how/why \(\displaystyle \frac{ r_g ( k(h) ) }{ |h| } \to 0\) as \(\displaystyle h \to 0\). ... ...
Help will be much appreciated ...Peter==============================================================================The above post mentions Proposition 8.13 ... Proposition 8.13 reads as follows:
View attachment 9414
View attachment 9415
Hope that helps ...
Peter
I am currently reading Chapter 8: Differentiable Maps and am specifically focused on Section 8.2 Differentials ... ...
I need some help in order to fully understand the proof of Theorem 8.15 ...
Theorem 8.15 and its proof read as follows:
View attachment 9412
View attachment 9413
In the above proof by Browder we read the following:" ... ... Then \(\displaystyle |k| \leq C |h|\) for \(\displaystyle |h|\) sufficiently small, if \(\displaystyle C \gt \| T \|\), by Proposition 8.13; it follows that
\(\displaystyle \frac{ r_g ( k(h) ) }{ |h| } \to 0\) as \(\displaystyle h \to 0\). ... ... "
My question is as follows:Can someone demonstrate formally and rigorously how/why \(\displaystyle \frac{ r_g ( k(h) ) }{ |h| } \to 0\) as \(\displaystyle h \to 0\). ... ...
Help will be much appreciated ...Peter==============================================================================The above post mentions Proposition 8.13 ... Proposition 8.13 reads as follows:
View attachment 9414
View attachment 9415
Hope that helps ...
Peter
Attachments
Last edited: