- #1
jakeowens
- 34
- 0
The return stroke of a bolt of lightning typically carries a peak current of 24 kA up from the ground. What is the maximum magnetic field associated with the bolt 1.4 m away?l;
I'm just having trouble finding the right formula for this problem
is the correct formula B= (4pi x 10^-7* I)/2pi * r?
giving me a magnetic field of .00343 T?
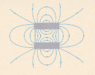
.] The field-line pattern around the two bars in Fig. MC1 shows that
*either both bars are permanent magnets with like poles adjacent, or one is permanent and one is a soft iron bar
*neither bar is a permanent magnet
*both must be identical permanently magnetized bars with opposite poles adjacent to each other
* none of these
* both bars must be permanent magnets with like poles adjacent to each other

For this one i said they must be identical permanent magnetzied bars with opposite poles adjacent to each other, i know they both have to be magnets, and the poles must be adjacent to each other or else the magnetic field lines would be repelled. I'm just not sure if one of them could be a soft iron bar. am i right?
I'm just having trouble finding the right formula for this problem
is the correct formula B= (4pi x 10^-7* I)/2pi * r?
giving me a magnetic field of .00343 T?
.] The field-line pattern around the two bars in Fig. MC1 shows that
*either both bars are permanent magnets with like poles adjacent, or one is permanent and one is a soft iron bar
*neither bar is a permanent magnet
*both must be identical permanently magnetized bars with opposite poles adjacent to each other
* none of these
* both bars must be permanent magnets with like poles adjacent to each other
For this one i said they must be identical permanent magnetzied bars with opposite poles adjacent to each other, i know they both have to be magnets, and the poles must be adjacent to each other or else the magnetic field lines would be repelled. I'm just not sure if one of them could be a soft iron bar. am i right?