Mustafa Bayram
- 7
- 0
when an electron is excited to the conduction band is it move further from the nucleus?
Are free electrons in the conduction band further from valence electrons?
I saw this picture that seems problematic to me. what do you think?
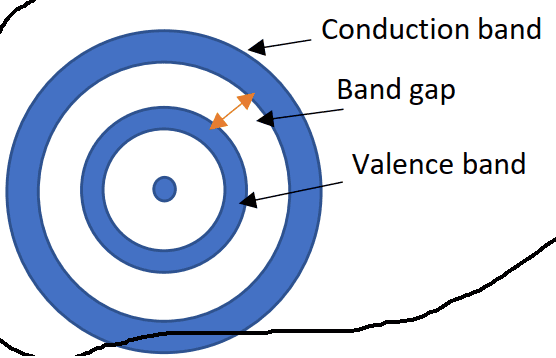
Are free electrons in the conduction band further from valence electrons?
I saw this picture that seems problematic to me. what do you think?