- #1
christian0710
- 409
- 9
Hi,
My textbooks says that "Josef Stefan investigated the increasing brightness of a black body as it is heated and discovered that the total intensity of radiation emitted over all wavelenghts increases as the fourth power of the aboslute temperature"
MY question is this: Is the "total intensity of radiation emitted over ALL wavelengths" the same as the ares (integral) underneath the Intensity vs wavelength graph that i posted underneath?
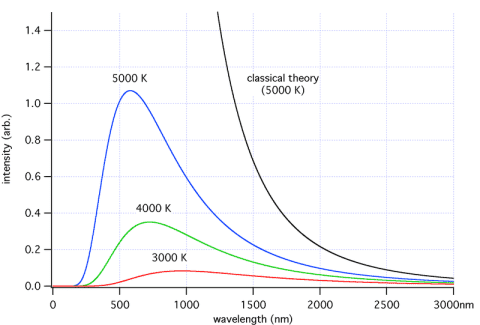
So the "TOTAL INTENSITY" it's NOT the peak intensity but the sum of all intensities from all the wavelengths that are emittet at that specific temperature?
My textbooks says that "Josef Stefan investigated the increasing brightness of a black body as it is heated and discovered that the total intensity of radiation emitted over all wavelenghts increases as the fourth power of the aboslute temperature"
MY question is this: Is the "total intensity of radiation emitted over ALL wavelengths" the same as the ares (integral) underneath the Intensity vs wavelength graph that i posted underneath?
So the "TOTAL INTENSITY" it's NOT the peak intensity but the sum of all intensities from all the wavelengths that are emittet at that specific temperature?