Anmoldeep
- 15
- 2
- Homework Statement
- Not exactly homework, this is a hard-to-understand concept for me about potentials in time-varying fields and converting them to explicitly position-dependent potentials.
- Relevant Equations
- n/a
Ion traps are very complex, but one of my Physics Olympiad textbooks presents a simplified model of a resonating charged particle in an ion trap
A tuned circuit consists of an inductor and a parallel plate capacitor (capacitance C and plate separation d). It has a resonating frequency ##\nu _{o}## What will be the resonating frequency if a particle P of mass m and charge q is inserted in the middle of the capacitor plates. Neglect effects of gravity, fringing of electric field, and electrostatic images.
So they basically neglected all obvious means of interaction, the only thing I can think of the charge's contribution to displacement current being the mode of interaction. But I won't be working with forces, rather an energy.
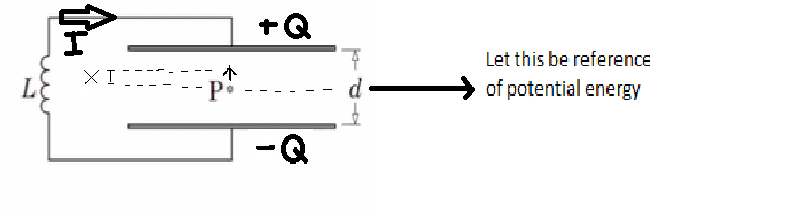 Since this is a coupled oscillator, I can write the energy of the system at any instant as
Since this is a coupled oscillator, I can write the energy of the system at any instant as
$$\frac{1}{2} LI^{2} +\frac{1}{2}\frac{Q^{2}}{C} +\frac{1}{2} mv^{2} +U( x,t) ={E _{total}} =Constant$$
Where $$U( x,t)$$ is the potential energy as a function of position (x) of charge from the middle of the capacitor and/or time (t). Since the charges on the capacitor plates are oscillating, defining potential energy the usual way seemed tough as there is a dependence on time, however since the system is coupled, time dependence is implicit and can be reduced to pure position dependence, hence allowing us to reason why the energy is conserved.
With this in mind, let's define all variables in the system as explicit functions of x, which is further a function of t. By doing this, the time-dependant electric field perfectly converts to a position-dependent field which looks like a static field hence allowing us to define potential energy. We will not consider the energy density of this new static field as its an imaginary construct.
The imaginary static field points towards the reference line at all times and has a varying magnitude that increases as we move towards one of the plates.
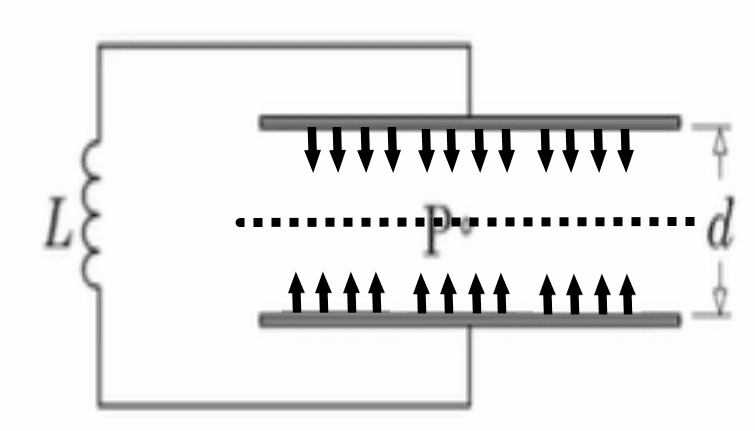
Now it's obvious, for resonance to take place we need stable oscillations with a restoring force, hence assuming the particle has a positive charge, when the particle is moving away from the mean position, it will move towards the positive plate, and when it is moving towards the mean position it will move towards the negative plate.
Therefore
$$U( x,t) =U( x) =\int _{0}^{x}\frac{Q_{y} q}{A\epsilon _{o}} .dy$$
I used y as a free variable and x as a bound variable to avoid confusion while differentiating.
Since the system is closed, I can say that at any position (x) of particle, total energy remains same.
$$\frac{d( E_{Total})}{dx} =0\ \ \Longrightarrow \ LI\frac{d( I)}{dx} +\frac{Q}{C}\frac{d( Q)}{dx} +mv\frac{d( v)}{dx} +\frac{d( U( x))}{dx} =0$$
$$mv\frac{d(v)}{dx} =-\frac{Q q}{A\epsilon _{o}} =force\ on\ charged\ particle$$
$$\frac{d( U( x))}{dx} =\frac{d\left(\int _{0}^{x}\frac{Q_{y} q}{A\epsilon _{o}} .dy\right)}{dx} =\frac{Q q}{A\epsilon _{o}} \ \ ( by\ Leibnitz\ rule\ of\ differentiation\ under\ the\ integral)$$
$$\frac{d( E_{Total})}{dx} =\ LI\frac{d( I)}{dx} +\frac{Q}{C}\frac{d( Q)}{dx} -\frac{Q q}{A\epsilon _{o}} +\frac{Q q}{A\epsilon _{o}} =0\Longrightarrow LI\frac{d( I)}{dx} +\frac{Q}{C}\frac{d( Q)}{dx} =0$$
Ok cool, this got lot less interesting since this just simplifies to the usual LC oscillations equation completely decoupled from the particle's motion.
This is not a coupled ion trap, its just a particle in an oscillating field over which it has no control.
A tuned circuit consists of an inductor and a parallel plate capacitor (capacitance C and plate separation d). It has a resonating frequency ##\nu _{o}## What will be the resonating frequency if a particle P of mass m and charge q is inserted in the middle of the capacitor plates. Neglect effects of gravity, fringing of electric field, and electrostatic images.
So they basically neglected all obvious means of interaction, the only thing I can think of the charge's contribution to displacement current being the mode of interaction. But I won't be working with forces, rather an energy.
$$\frac{1}{2} LI^{2} +\frac{1}{2}\frac{Q^{2}}{C} +\frac{1}{2} mv^{2} +U( x,t) ={E _{total}} =Constant$$
Where $$U( x,t)$$ is the potential energy as a function of position (x) of charge from the middle of the capacitor and/or time (t). Since the charges on the capacitor plates are oscillating, defining potential energy the usual way seemed tough as there is a dependence on time, however since the system is coupled, time dependence is implicit and can be reduced to pure position dependence, hence allowing us to reason why the energy is conserved.
With this in mind, let's define all variables in the system as explicit functions of x, which is further a function of t. By doing this, the time-dependant electric field perfectly converts to a position-dependent field which looks like a static field hence allowing us to define potential energy. We will not consider the energy density of this new static field as its an imaginary construct.
The imaginary static field points towards the reference line at all times and has a varying magnitude that increases as we move towards one of the plates.
Now it's obvious, for resonance to take place we need stable oscillations with a restoring force, hence assuming the particle has a positive charge, when the particle is moving away from the mean position, it will move towards the positive plate, and when it is moving towards the mean position it will move towards the negative plate.
Therefore
$$U( x,t) =U( x) =\int _{0}^{x}\frac{Q_{y} q}{A\epsilon _{o}} .dy$$
I used y as a free variable and x as a bound variable to avoid confusion while differentiating.
Since the system is closed, I can say that at any position (x) of particle, total energy remains same.
$$\frac{d( E_{Total})}{dx} =0\ \ \Longrightarrow \ LI\frac{d( I)}{dx} +\frac{Q}{C}\frac{d( Q)}{dx} +mv\frac{d( v)}{dx} +\frac{d( U( x))}{dx} =0$$
$$mv\frac{d(v)}{dx} =-\frac{Q q}{A\epsilon _{o}} =force\ on\ charged\ particle$$
$$\frac{d( U( x))}{dx} =\frac{d\left(\int _{0}^{x}\frac{Q_{y} q}{A\epsilon _{o}} .dy\right)}{dx} =\frac{Q q}{A\epsilon _{o}} \ \ ( by\ Leibnitz\ rule\ of\ differentiation\ under\ the\ integral)$$
$$\frac{d( E_{Total})}{dx} =\ LI\frac{d( I)}{dx} +\frac{Q}{C}\frac{d( Q)}{dx} -\frac{Q q}{A\epsilon _{o}} +\frac{Q q}{A\epsilon _{o}} =0\Longrightarrow LI\frac{d( I)}{dx} +\frac{Q}{C}\frac{d( Q)}{dx} =0$$
Ok cool, this got lot less interesting since this just simplifies to the usual LC oscillations equation completely decoupled from the particle's motion.
This is not a coupled ion trap, its just a particle in an oscillating field over which it has no control.