Viona
- 49
- 12
- Homework Statement
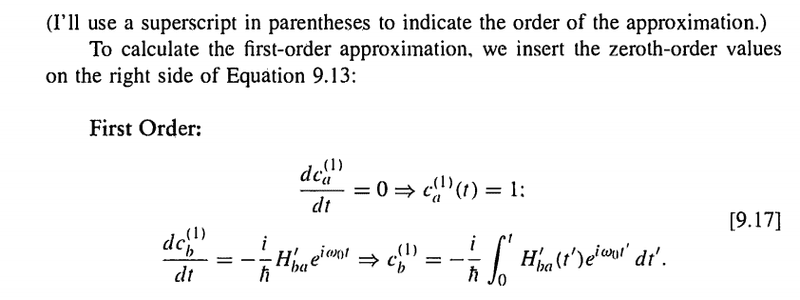
- Why the first-order correction equals 1 instead of arbitrary constant?
- Relevant Equations
- Why the first-order correction equals 1 instead of arbitrary constant?
I was reading in the Book: Introduction to Quantum Mechanics by David J. Griffiths. In chapter Time-Dependent Perturbation Theory, Section 9.12. I could not understand that why he put the first order correction ca(1)(t)=1 while it equals a constant.