- #1
aznmax218
- 1
- 0
Determine the turns ratios a1 and 12 for maximum power transfer to the 20 ohm load resistor. a=n2/n1; Rs=RL for maximum power transfer, i.e. Zsource = the complex conjugate of the load.
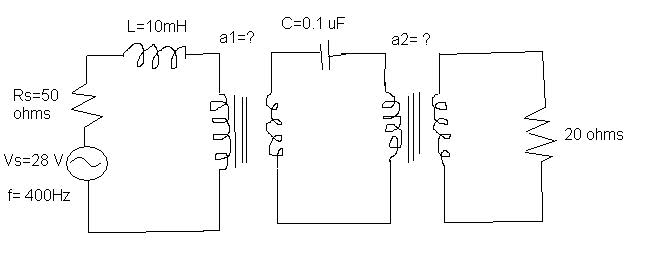 i have try to use
i have try to use
Z1=a1^2*Zs and Z2=a2^2*Z1
and i know Z1=-j/(2*pi*f*c)
Z1=a1^2*Zs and Z2=a2^2*Z1
and i know Z1=-j/(2*pi*f*c)