- #1
septentriones
- 3
- 0
Homework Statement
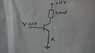
consider the following circuit:
a) Determine the value of the resistor, R so that a current of 0.5 A flows through the load.
b) What is the maximum value of th load resistor?
c) If the load resistor is 10Ω, what value of VB will put the transistor into saturation?
Homework Equations
IC ≈ IE = VE/RE
IC ≈ (VB-0.6V)/RE
ICRL+VCE+VE=Vcc
The Attempt at a Solution
a) 0.5 ≈ (3.2 - 0.6)/RE
RE = 5.2Ω
b) (I am guessing that the VCE is 0.6 V here but I am not sure)
0.5RL+0.6+0.5 = 15
RL = 27.8Ω
c) From what I can tell, the transistor is an NPN and in that case, in order to saturate it, the base voltage must be greater than the collector or emitters'.
VC=ICRC
VC=(0.5)(27.8)=13.9V
VE=IERE
VE=(0.5)(5.2)=2.6V
So in order to be greater than both the VB must be greater than 13.9V
Parts b and c I was not so sure about, thanks for any input.
(Sorry that the image is not nicely sized, I'm not sure how to fix it.)