- #1
reddvoid
- 119
- 1
Homework Statement
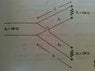
Here R1 and R2 are to be fed in phase from a 100 ohm line with R1 receiving twice the power of R2 ...how to find Z1 and l1
Z2 and l2
to find power delivered to load we need transmission coefficient ??
i don't understand the meaning of "fed in phase"