- #1
annm95
- 1
- 0
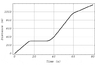
A car travels a certain distance along a straight road (in the +x direction). The distance the car travels as a function of time is shown in the figure below.
When the car changes speed it does so uniformly.
Select the appropriate choice for each statement: T-True, F-False, G-Greater than, L-Less than, E-Equal to. (If the first is T, the second is G, and the rest E, enter TGE
This is what I got and my reasoning behind them but I keep getting it wrong. Is there a certain equation to find the answers?
The speed is ... zero at 20 sec. (E) At 20 seconds, there is no slope, which indicates the speed is zero.
At 48 sec, the speed is as high as it gets. (T) The area around 48 seconds is the steepest part of the graph, which shows that the speed is highest at that point.
The speed at 4 sec is ... the speed at 76 sec. (G) The slope is steeper at 4 seconds than it is at 76 seconds, which indicates that the speed is greater at 4 seconds.
The acceleration magnitude at 15 sec is ... the acceleration magnitude at 37 sec. (L) At 15 sec, the curve looks smooth and spread out, but at 37 sec, the curve looks sharper and tighter, which indicates that the acceleration magnitude is less at 15 seconds.
The x-acceleration is ... zero at 58 sec (G) The slope is positive at 58 seconds, so it is accelerating and therefore greater than zero.
The x-acceleration is ... zero at 50 sec (G) The slope is positive at 50 seconds, so it is accelerating and therefore greater than zero
When the car changes speed it does so uniformly.
Select the appropriate choice for each statement: T-True, F-False, G-Greater than, L-Less than, E-Equal to. (If the first is T, the second is G, and the rest E, enter TGE
This is what I got and my reasoning behind them but I keep getting it wrong. Is there a certain equation to find the answers?
The speed is ... zero at 20 sec. (E) At 20 seconds, there is no slope, which indicates the speed is zero.
At 48 sec, the speed is as high as it gets. (T) The area around 48 seconds is the steepest part of the graph, which shows that the speed is highest at that point.
The speed at 4 sec is ... the speed at 76 sec. (G) The slope is steeper at 4 seconds than it is at 76 seconds, which indicates that the speed is greater at 4 seconds.
The acceleration magnitude at 15 sec is ... the acceleration magnitude at 37 sec. (L) At 15 sec, the curve looks smooth and spread out, but at 37 sec, the curve looks sharper and tighter, which indicates that the acceleration magnitude is less at 15 seconds.
The x-acceleration is ... zero at 58 sec (G) The slope is positive at 58 seconds, so it is accelerating and therefore greater than zero.
The x-acceleration is ... zero at 50 sec (G) The slope is positive at 50 seconds, so it is accelerating and therefore greater than zero
Attachments
Last edited: