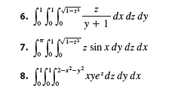karush
Gold Member
MHB
- 3,240
- 5
View attachment 9379
ok this is a snip from stewards v8 15.6 ex
hopefully to do all 3 here
$\displaystyle\int_0^1\int_{0}^{1}\int_{0}^{\sqrt{1-x^2}}\dfrac{z}{y+1} \,dxdzdy$
so going from the center out but there is no x in the integrand
$\displaystyle\int_0^{\sqrt{1 - x^2}} \dfrac{z}{y + 1}dx =\dfrac{ \sqrt{1 - x^2} z}{y + 1}$
and
$\displaystyle\int_0^1 \dfrac{ \sqrt{1 - x^2} z}{y + 1} \, dz=\frac{\sqrt{1-x^2}}{2\left(1+y\right)} $
kinda maybe so far?
ok this is a snip from stewards v8 15.6 ex
hopefully to do all 3 here
$\displaystyle\int_0^1\int_{0}^{1}\int_{0}^{\sqrt{1-x^2}}\dfrac{z}{y+1} \,dxdzdy$
so going from the center out but there is no x in the integrand
$\displaystyle\int_0^{\sqrt{1 - x^2}} \dfrac{z}{y + 1}dx =\dfrac{ \sqrt{1 - x^2} z}{y + 1}$
and
$\displaystyle\int_0^1 \dfrac{ \sqrt{1 - x^2} z}{y + 1} \, dz=\frac{\sqrt{1-x^2}}{2\left(1+y\right)} $
kinda maybe so far?
Attachments
Last edited: