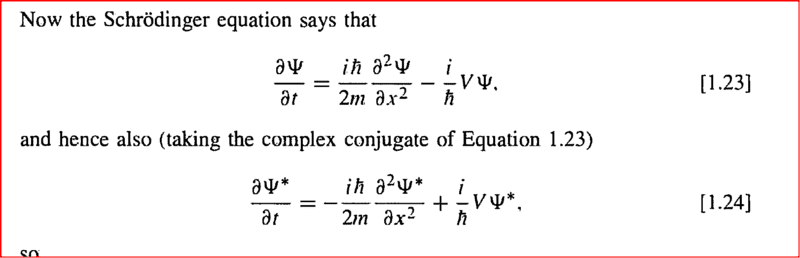RahSuh
- 10
- 4
- Homework Statement
- Page 13 of Griffiths on Quantum Mechanics ( the part on Normalization)
- Relevant Equations
- Am look at the proof of normalised solns of Schrodingers Eqn stay normalised
Am looking at page 13 of QM by Griffiths - have become stuck on minor point. He is proving that a normalised solution of Schrodingers eqn stays normalised. The bit I don't get is how can you just take the complex conjugate of Schrodingers eqn and assume its true. (ie how does he get from Eqn 1.23 to Eqn 1.24) I assume it true but how ? I get that for example, the complex conjugate of the product of 2 complex numbers is the product of the complex conjugates etc - but does it apply to differential eqns. Can you just take the complex conjugates of differential eqns. Thanks for help in advance! (am sure its something very simple)