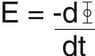- #1
fran1942
- 80
- 0
Hello, our tutor gave us this equation for Faradays law, but I don't quite understand it's composition. (I have attached a graphic of the equation)
Can someone please tell me what the -d and dt represent ?
Also, what does the E stand for ? I thought it should be I (current).
Thanks kindly for any help.
Can someone please tell me what the -d and dt represent ?
Also, what does the E stand for ? I thought it should be I (current).
Thanks kindly for any help.