- #1
kachi
- 9
- 0
Hello. I have had an attempt at solving this pressure drop problem, but I have been told it is incorrect.
I am very much a beginner in the area of fluid mechanics, so if you could please define any terms that you are using, that would be so helpful!
I thought using the Hagen-Poiseuille would fit, as the question has given data that would fit into the equation and it also suggests that the pipe is laminar (smooth pipe). Although, it does not state whether the pipe has bends or is just straight. Does 'smooth pipe' also mean 'straight pipe'? Do I assume its straight?
Why is my attempt wrong? What are the other possible ways to solve this/pressure drop?
The lecturer I asked said that this method wasn't right, and that I should just calculate pressure multiplied by all the heads (pressure x heads). I still am confused by this though.
Also, am I allowed to ask more questions relating to my given question in this thread?
The question is below:
Water at 20°C flows in a 35 cm diameter smooth pipe at a rate of 0.0476 m^3/s from the Goulburn River to the Holding tank. What is the frictional head lost* (in m) and corresponding pressure drop (in kPa) per 100m length of pipe?
EDIT: *I didn't see this part of the question...
Known data:
Hagen-Poiseuille equation:
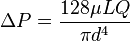
Where:
ΔP is the pressure loss
L is the length of pipe
μ is the dynamic viscosity
Q is the volumetric flow rate
d is the diameter
Pi is the mathematical constant Pi
Using:
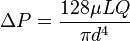
Where:
ΔP is the pressure loss (Pa) = ?
L is the length of pipe (m) = 100m
μ is the dynamic viscosity (Pa*s) = 1.002 for Water @ 20°C
Q is the volumetric flow rate (m^3/s) = 0.0476 m^3/s
d is the diameter (m) = 0.35m
Pi is the mathematical constant Pi Attempt:
ΔP = (128(1.002 Pa*s)(100m)(0.0476 m^3/s))/pi(0.35)^4
= 12949.786 Pa
ΔP = 12.95 kPa/100m
Pressure drop is 12.95 kPa per 100m length of pipe.
Thank you very much in advance. I appreciate it.
I am very much a beginner in the area of fluid mechanics, so if you could please define any terms that you are using, that would be so helpful!
I thought using the Hagen-Poiseuille would fit, as the question has given data that would fit into the equation and it also suggests that the pipe is laminar (smooth pipe). Although, it does not state whether the pipe has bends or is just straight. Does 'smooth pipe' also mean 'straight pipe'? Do I assume its straight?
Why is my attempt wrong? What are the other possible ways to solve this/pressure drop?
The lecturer I asked said that this method wasn't right, and that I should just calculate pressure multiplied by all the heads (pressure x heads). I still am confused by this though.
Also, am I allowed to ask more questions relating to my given question in this thread?
The question is below:
Homework Statement
Water at 20°C flows in a 35 cm diameter smooth pipe at a rate of 0.0476 m^3/s from the Goulburn River to the Holding tank. What is the frictional head lost* (in m) and corresponding pressure drop (in kPa) per 100m length of pipe?
EDIT: *I didn't see this part of the question...
Known data:
- Water has a temperature of 20°C
- Diameter of pipe is 35cm
- Flow rate is 0.0476 m^3/s
- Length of pipe is 100m
Homework Equations
Hagen-Poiseuille equation:
Where:
ΔP is the pressure loss
L is the length of pipe
μ is the dynamic viscosity
Q is the volumetric flow rate
d is the diameter
Pi is the mathematical constant Pi
The Attempt at a Solution
Using:
Where:
ΔP is the pressure loss (Pa) = ?
L is the length of pipe (m) = 100m
μ is the dynamic viscosity (Pa*s) = 1.002 for Water @ 20°C
Q is the volumetric flow rate (m^3/s) = 0.0476 m^3/s
d is the diameter (m) = 0.35m
Pi is the mathematical constant Pi Attempt:
ΔP = (128(1.002 Pa*s)(100m)(0.0476 m^3/s))/pi(0.35)^4
= 12949.786 Pa
ΔP = 12.95 kPa/100m
Pressure drop is 12.95 kPa per 100m length of pipe.
Thank you very much in advance. I appreciate it.
Last edited: