- #1
kvanr
- 7
- 0
Homework Statement
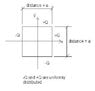
Electric charge is distributed along each side of a square. Two adjacent sides have positive charge +Q on each, two sides have -Q on each.
What are the x and y components of the net electric field at the center of the square? (Each side has length "a").
Homework Equations
E=F/q ?
F=k*q1*q2/r^2
k=9E9Nm^2/C^2
The Attempt at a Solution
Trying to come up with a differential equation? I don't know how to begin with having 4 sides.