- #1
freshcoast
- 185
- 1
1. Problem statement, all variables and given/known data.
A 25kg box of books is in the back of the truck. The truck-box system has frictional coefficients (static = 0.4, kinetic = 0.25). You get in the truck and begin to drive in a straight line. Under these conditions
a) After reaching your final cruising speed of 25 m/s and reach the top of long downhill section of road with a constant slope. In order to avoid a collision you tap your brakes, and the box slips and then slides towards the front of the truck with a constant speed. What is the angle of the hill?
b) As you drive your truck over the top of a semi circular hill at a speed of 50km/hr, what is the magnitude of the maximum possible static friction force acting on the box?
2. Homework Equations .
F = ma
Vf = vo + at
X = vo^2 + 1/2at^2
Vf^2 = vo^2 + 2ax
3. Attempt at solutionFor part a) drew FBD, separated the components and moved things around to find the angle.
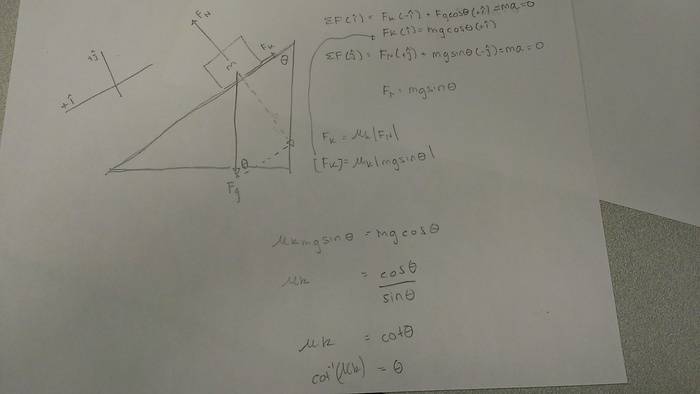
For part b) drew FBD, separated components and used the radial equation for force to find the static friction force.
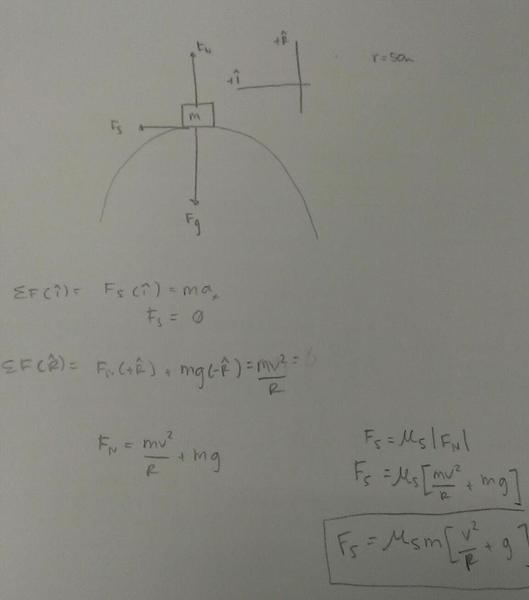
Thanks in advance for any input
A 25kg box of books is in the back of the truck. The truck-box system has frictional coefficients (static = 0.4, kinetic = 0.25). You get in the truck and begin to drive in a straight line. Under these conditions
a) After reaching your final cruising speed of 25 m/s and reach the top of long downhill section of road with a constant slope. In order to avoid a collision you tap your brakes, and the box slips and then slides towards the front of the truck with a constant speed. What is the angle of the hill?
b) As you drive your truck over the top of a semi circular hill at a speed of 50km/hr, what is the magnitude of the maximum possible static friction force acting on the box?
2. Homework Equations .
F = ma
Vf = vo + at
X = vo^2 + 1/2at^2
Vf^2 = vo^2 + 2ax
3. Attempt at solutionFor part a) drew FBD, separated the components and moved things around to find the angle.
For part b) drew FBD, separated components and used the radial equation for force to find the static friction force.
Thanks in advance for any input