SpectraPhy09
- 23
- 3
- Homework Statement
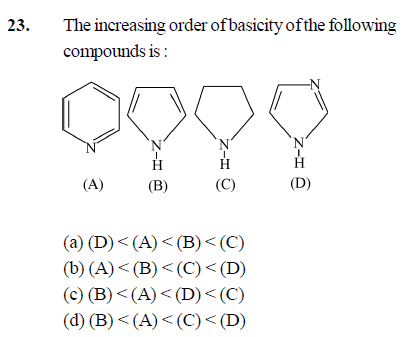
- the increasing order of the basicity of the following
compounds : (Please check the image I have attached for the options )
- Relevant Equations
- I don't know any
I think the correct ans should be c (i.e C>D>A>B ) but its given d in my textbook( There can be a error also but I'm sure)
I think C should have the highest basic strength since Hybridisation of N in this is Sp3 so it has the least electronegativity so it can donate its lone pair easily
Then it should be D since there are two N atoms of which one's lone pair is in conjugation and one has a lone pair not in conjugation so it can donate that lone pair
Then A because it has only One N atom of whose lone pair is not in the conjugation. So it can donate it. And B last because the lone of N atom here is involved in the Aromaticity of the compound so it would be very difficult for it to donate that lone pair
Plz, can someone tell me if my reasoning is correct?
I think C should have the highest basic strength since Hybridisation of N in this is Sp3 so it has the least electronegativity so it can donate its lone pair easily
Then it should be D since there are two N atoms of which one's lone pair is in conjugation and one has a lone pair not in conjugation so it can donate that lone pair
Then A because it has only One N atom of whose lone pair is not in the conjugation. So it can donate it. And B last because the lone of N atom here is involved in the Aromaticity of the compound so it would be very difficult for it to donate that lone pair
Plz, can someone tell me if my reasoning is correct?
Last edited by a moderator: