- #1
connor02
- 27
- 0
Homework Statement
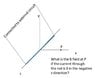
I have attached a diagram with the question.
Homework Equations
Biot-Savart law: (μ/4π)(I/r^2)(dlxr) or (μ/4π)(q/r^2)(dvxr)
The Attempt at a Solution
My question is,
The B field can be predicted from the right hand corkscrew rule right? So the part of the rod that exerts a B field on point P is only the small portion of the rod at the origin right?
The answer key shows some intergral over the whole length of the rod which I do not understand as I think the part of the rod that creates a B field at point P is only the little bit at the origin.
Thanks.