- #1
sina_mech
- 13
- 0
hi friends , please help me to solve this problem , THANKS :
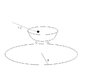
A ball with radius r and mass m with angel 30 with horizon and with velocity V, according to figure, enters to a semispherical shell with radius R and the coefficient of friction between semispherical shell and ball is µ . This semispherical shell is in the Car moving at the circular path with radius a .assume that the semispherical shell is without any linear or lateral movement on the car:
A: assume that the velocity of car and the semispherical shell is zero, and determine the path of the Ball’s movement.
B: assume that the semispherical shell rotate about its z-axe with constant angular velocity of w1 and determine the path of the Ball’s movement.
C: assume that the semispherical shell rotate about its z-axe with angular velocity of w1, and the car moves in circular path with constant angular velocity of w2. Determine the path of the Ball’s movement.
A ball with radius r and mass m with angel 30 with horizon and with velocity V, according to figure, enters to a semispherical shell with radius R and the coefficient of friction between semispherical shell and ball is µ . This semispherical shell is in the Car moving at the circular path with radius a .assume that the semispherical shell is without any linear or lateral movement on the car:
A: assume that the velocity of car and the semispherical shell is zero, and determine the path of the Ball’s movement.
B: assume that the semispherical shell rotate about its z-axe with constant angular velocity of w1 and determine the path of the Ball’s movement.
C: assume that the semispherical shell rotate about its z-axe with angular velocity of w1, and the car moves in circular path with constant angular velocity of w2. Determine the path of the Ball’s movement.